Neurotherapy Overview
Neurotherapy, also called Neurofeedback (NFB), Biofeedback, or Brainwave Training is a type of alternative therapy that uses real-time displays of electroencephalography (EEG) to illustrate brain activity. By recording brain wave activity using sensors placed on the head, our doctors can gather information about why you may be having clinical symptoms based on what is happening in your brain.
States of neurophysiological over-arousal or under-arousal can contribute to why you may be manifesting symptoms of anxiety, depression, attention deficit disorder (ADD/ADHD), and a variety of other stressful conditions.
Once initial information has been gathered from 19 specific sites on your head, neurofeedback can be used to track your brain wave activity, and train your brain to operate more efficiently by providing you with visual and auditory feedback as your brain wave patterns improve and self-regulation occurs.
The neurofeedback training is accomplished via experiencing visual stimulation that darkens and lightens as brainwave patterns change. By adjusting the brightness with your brainwaves you retrain then and engage brain. Over the course of the neurofeedback treatment, neuroplasticity creates permanent positive changes.
Our Unique Integrated Approach
Unlike the drugs-only method to treatment favored by a typical physician, our individualized, comprehensive approach addresses the mental, emotional and physical areas of each patient in our care. In our many years of experience working with hundreds of patients, we found unequivocally that it is only by taking a more holistic approach to treatment that optimal results can be obtained and even more importantly sustained.
Want To See How Neurotherapy Can Help? Book a Free Consultation Today!
How The Brain Works
In order to understand how Neurotherapy works we first need to understand how the brain works. The systems that govern the human brain are the most complex and compact on earth.
In order for the brain to function optimally, the parts of the brain must talk to one another effectively. The brain accomplishes this communication by transmitting electrical signals along neurons that connect one area of the brain to another. The electrical signals are expressed as brain waves.
Neurofeedback therapy corrects the signal messaging to create the desired state change in the brain which is what alleviates the conditions treated through a process known as brain plasticity. Neuroplasticity, or brain plasticity, refers to the brain's ability to change throughout life. The key concept behind neuroplasticity is “neurons that fire together wire together”.
The idea is that when two events (neurons firing) occur in the brain at the same time, the events (neurons) become associated with one another, and the neuronal connections (wiring) become stronger. Neurofeedback therapy helps to both regulate brainwave patterns to a more desirable balanced state as well as assists in the process of neuroplastic change.
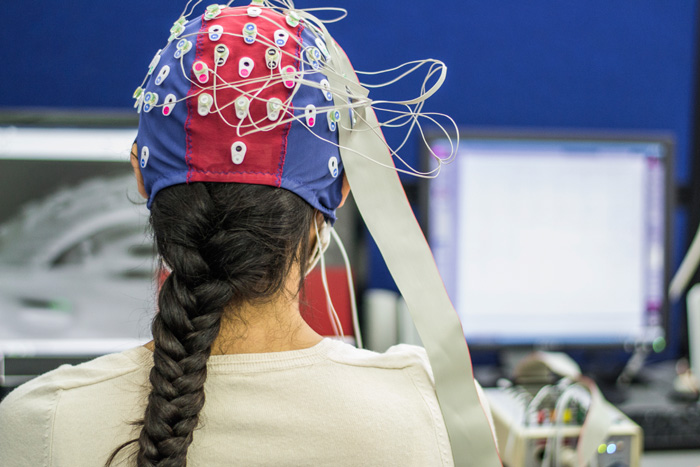
QEEG Testing
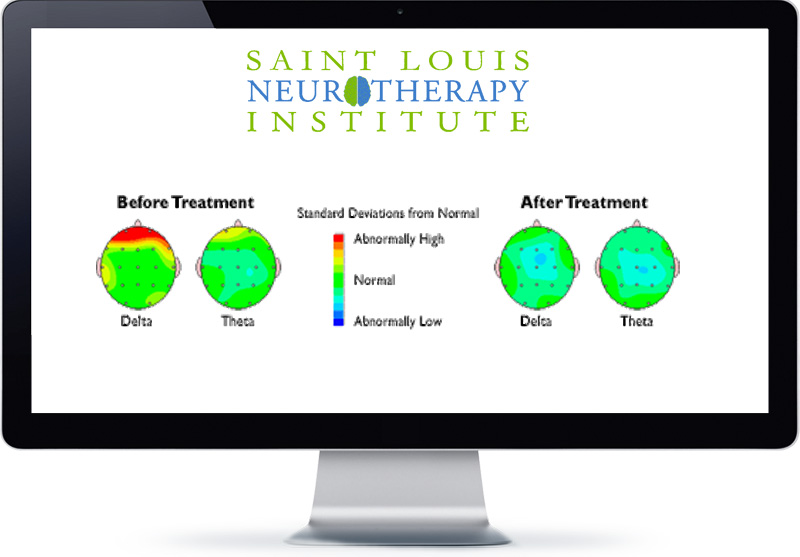
Using a QEEG (quantitative electroencephalography), our clinicians first obtain detailed baseline information regarding activity levels in each area of the brain. To gather this data, patients briefly wear a “swim cap” that houses 19 leads which painlessly read different areas of the brain. These leads hold sensors which loop back to the computer, registering the specific levels of activity. The totality of these readings produces what is called a QEEG brain map, specific to the individual patient.
We can see what is actually happening inside the brain for a truly accurate insight of what is creating the issues. From this baseline we can customize a treatment program for maximum results.
Want To See How Neurotherapy Can Help? Book a Free Consultation Today!
The Retraining Process
Once the QEEG brain map is analyzed, a protocol is chosen based upon the patient’s specific brain map. The neurotherapist identifies specific parameters for brain waves to meet and inputs them into the computer system. Patients then have sensors placed on their head at the training sites associated with their areas of dysfunction. While viewing a video/DVD of choice, patients must maintain the brainwave states as defined by the neurotherapist to keep the video from fading (operant conditioning). When the brainwaves fall into the given parameters, the screen brightens (reward). When the brainwaves move beyond the parameters, the movie dims. Thus, a feedback loop is created, reinforcing positive shifts in brainwave activity time and time again, creating new, permanent, neuropathways.